Tankless water heaters, also known as demand-type or instantaneous water heaters, have transformed the traditional concept of water heating. These ingenious devices supply hot water only when needed, making them more energy-efficient than their storage tank counterparts. The crux of their operation lies in their compact yet sophisticated design, which we will decode in this article.
Instantaneous water heaters offer an endless supply of hot water while conserving energy and minimizing bills. At the core of their operation are intricate mechanisms and components, whose synergy facilitates efficient heating. The highlight, undoubtedly, is the minimalism they bring to the water heating sector, juxtaposed with their effective functionality.
While these heaters represent modern engineering marvels, understanding their operation doesn’t necessitate a technical background. Our exploration will demystify the enigma surrounding the tankless water heater diagram, encompassing its basic structure, functionality, and relevant information on various types of these heaters.
Contents
Advantages of Tankless Water Heaters
Compact Design and Functionality
Tankless water heaters pack an impressive amount of technology into their small form factor. The streamlined design enables them to fit in limited spaces, a far cry from traditional bulky tank heaters. Their operation is equally efficient, providing hot water on demand without maintaining a stored water supply.
Energy Efficient Features
Their energy efficiency results from the absence of standby heat loss, which plagues traditional water heaters. Energy is only utilized when hot water is needed, making them up to 24-34% more energy-efficient for homes using 41 gallons or less of hot water daily.
Lifespan and Durability
Due to fewer components exposed to constant water, tankless heaters can outlast their tank counterparts, with a typical lifespan exceeding 20 years. Furthermore, they offer replaceable parts, which can further extend their useful life.
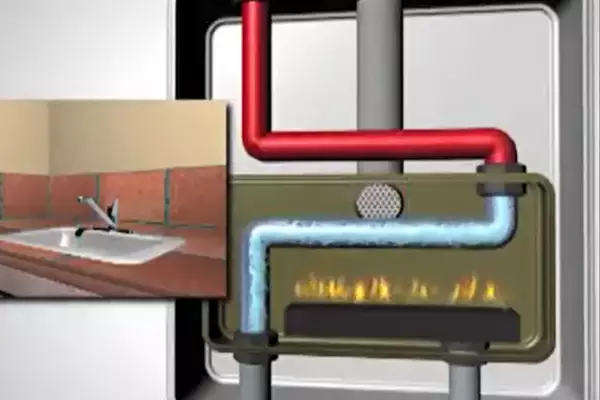
Tankless Water Heater Basics
Core Components of a Tankless System
At the heart of a tankless system lie three critical components: the heat exchanger, flow sensor, and the control panel. The heat exchanger initiates the heating process once activated, while the flow sensor detects water flow, triggering the heater.
The Role of Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are copper or stainless-steel units that transfer heat from a heating element to the water. Once the flow sensor triggers the heater, the exchanger rapidly heats the water passing through it.
Flow Sensor Functions
Flow sensors detect when a hot water tap is turned on. Once detected, they signal the control panel, activating the heat exchanger to start heating the water.
Inside an Instantaneous Water Heater
Structure and Working Mechanism
An instantaneous water heater activates only when hot water is needed. It starts with the flow sensor detecting water flow, which activates the heater. The water is rapidly heated in the heat exchanger before being sent to the tap.
Sensing Flow and Heating
The flow sensor and heat exchanger work in unison to facilitate instantaneous heating. The moment hot water demand is detected, the heating process is initiated.
Safety Features Explained
Safety features in these heaters include temperature sensors and high-limit switches. The former regulates the water temperature, while the latter shuts off the heater if unsafe temperatures are reached.

Electric Tankless Water Heater Uncovered
Electric Power and Water Heating
Electric tankless water heaters employ electric resistance coils to heat the water. They are ideal for homes with limited space as they offer smaller sizes compared to gas heaters.
Component Comparison: Gas vs. Electric
Unlike gas heaters, electric units don’t require venting. They have fewer components, translating into lower maintenance needs. However, they often require a substantial amount of electrical capacity to operate.
Special Features of Electric Systems
Electric heaters offer modulating control. This allows them to adjust the power to meet the precise demand for hot water, enhancing their energy efficiency.
Instant Water Heater: How It Works
About Instant Heating
Instant heaters, as the name suggests, deliver hot water without delay. By superheating water as it flows through the unit, they eliminate the waiting time typically associated with traditional tank heaters.
Component Analysis: Inside an Instant Heater
An instant heater has similar components as a tankless system – a flow sensor, heat exchanger, and a control panel. However, the process is faster, offering hot water almost instantaneously.
Energy Savings and Cost-effectiveness
The absence of standby heat loss, coupled with the efficient operation of instant heaters, results in significant energy savings. These savings, over time, can offset their initial high investment cost.
Hot Water Heater Diagram: Decoding the Process
Heat Source and Transfer
In a hot water heater, the heat source (gas burner or electric element) heats the water. This heat is transferred to the water via the heat exchanger, delivering hot water to the outlet.
Hot Water Production and Delivery
The heater produces hot water once the tap is turned on, sending cold water into the unit, where it gets heated instantly before delivery to the faucet.
The Role of Thermostats and Safety Valves
Thermostats regulate the water temperature, while safety valves release pressure, preventing potential damage due to excessive pressure.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular Upkeep for Efficiency
Regular maintenance includes flushing the unit to remove scale build-up and checking for leaks. This helps maintain efficiency and extends the heater’s lifespan.
Common Issues and Solutions
Common problems include inadequate hot water, fluctuating temperatures, and system shut down. Most issues can be resolved by resetting the heater, cleaning the inlet screen, or adjusting the temperature dial.
Professional vs DIY Fixes
While minor issues like cleaning the inlet screen can be done at home, complex problems may require professional assistance. Always consult your manual or a professional when in doubt.
The Future of Water Heating
Technological Advancements and Innovations
The future of water heating lies in further enhancing efficiency and convenience. Advancements in heat pump technology, Wi-Fi enabled controls, and energy recovery systems are expected to take center stage.
Sustainability: The Green Heating Solutions
Green solutions like solar-powered heaters and hybrid systems aim to reduce the environmental impact of water heating. These systems combine environmental responsibility with advanced technology.
What to Expect in Upcoming Years
With a greater focus on sustainability and energy efficiency, expect to see more innovative, eco-friendly water heating solutions in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I service my tankless water heater?
Most manufacturers recommend servicing once a year. However, if you live in a hard water area, consider servicing twice a year to prevent scale build-up.
Are tankless water heaters more efficient than tank ones?
Yes, tankless water heaters are more efficient as they only heat water when needed, eliminating standby heat loss.
Do tankless water heaters provide hot water instantly?
Instantaneous or instant water heaters provide hot water without delay. However, the water must still travel from the heater to the faucet, which might take a few seconds.
Conclusion
Tankless water heaters embody a revolutionary shift in water heating technology. Their compact design, energy efficiency, and sophisticated components make them a preferred choice for modern households.
While their operation may appear complex, it is essentially a synergistic effort of various components working in harmony. From detecting water flow to rapid heating and delivery, every step is finely tuned for optimal performance.
